Learn: English can hide the person and still tell the full story. Watch closely to see how.
Revise: you studied Present Simple (active voice) in form 3. Revise it here: Present Simple
Key Takeways:
1. English has two voices: active and passive. Most sentences in English use the active voice, but sometimes English uses the passive voice.
Active voice: focuses on who does the action
My dad drives me to school.
Passive voice: focuses on what happens
I am driven to school.
Active voice: focuses on who does the action
My dad drives me to school.
Passive voice: focuses on what happens
I am driven to school.
2. We use the passive voice when the action is more important than the person. The passive voice is used when:
- the action matters more than the agent;
- we don’t know who did the action
Example: Dinner is cooked every weekend. (The focus is on the result (dinner), not on who cooked it.)
3. Form of the Present Simple Passive. The structure of the present simple passive is:
subject + am / is / are + past participle
Examples:
The house is cleaned by Alex.
Trees are planted by volunteers.
I am driven to school.
subject + am / is / are + past participle
Examples:
The house is cleaned by Alex.
Trees are planted by volunteers.
I am driven to school.
4. How to change an active sentence into a passive sentence
The object of the active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence.
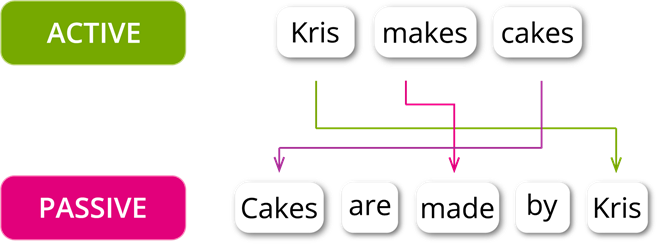
The object of the active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence.

5. The person (agent) is optional. In passive sentences:
- the person who did the action is often not mentioned;
- the agent is added only if it is important
Example:
The house is cleaned.
The house is cleaned by Alex.
The house is cleaned.
The house is cleaned by Alex.
6. Passive voice can be affirmative, negative, or a question.
Affirmative
Mobile phones are allowed.
Trees are planted by volunteers.
Mobile phones are allowed.
Trees are planted by volunteers.
Negative
Form:
subject + am/is/are + not + past participle
Examples:
Mobile phones aren’t allowed.
Laptops aren’t sold here in this shop.
Form:
subject + am/is/are + not + past participle
Examples:
Mobile phones aren’t allowed.
Laptops aren’t sold here in this shop.
Questions
Form:
(question word)* +am/is/are + subject + past participle
Examples:
Is English spoken in Holland?
Why are the dogs walked by Mila?
Form:
(question word)* +am/is/are + subject + past participle
Examples:
Is English spoken in Holland?
Why are the dogs walked by Mila?
7. Short answers use the verb “to be”
Are these cakes made by professional bakers?
— Yes, they are.
Is a new episode released every week?
— No, it isn’t.
Are these cakes made by professional bakers?
— Yes, they are.
Is a new episode released every week?
— No, it isn’t.
Question words* in English:
Watch the video and learn:
In summary:
Who — [huː] — asks about a person or people; kas, kurš, kuri
Who is your English teacher?
What — [wɒt] — asks about a thing, idea, or action; kāds, kas
What do you do?
Where — [weər] — asks about a place or location; kur, kurp
Where does she live?
When — [wen] — asks about time (date, day, moment); kad
When is your birthday?
Why — [waɪ] — asks about a reason or cause; kāpēc, kādēļ
Why are you late?
How — [haʊ] — asks about method, way, condition, or manner; kā, kādā veidā
How do you usually study?
Which — [wɪtʃ] — asks about a specific choice from a limited group; kurš, kāds
Which book do you want?
Whose — [huːz] — asks about ownership or possession; kā, kura, kuru
Whose bag is this?
...
Atsauce:
HUB Scuola "Video rule - Present Simple Passive" on youtube.com
British Council "Question words and WHEN to use them - a Mini English Lesson" on youtube.com